A SIC code refers to the classification of companies in the United Kingdom and in the United States. Like the NACE code, its European equivalent, it is made of letters and numbers. In addition to its use for statistical purposes by governments, it is also useful to companies for their marketing activities.
SIC Codes Definition
" SIC Codes" is an acronym for “Standard Industrial Classification Codes”. It refers to a nomenclature created in 1937 in the United States and introduced in the United Kingdom in 1948. SIC codes are used to classify companies according to their core activity.
SIC Code USA
The Standard Industrial Classification system has been integral in classifying industries based on their primary business activities. All businesses have a primary SIC code. This is the main code that categorizes the core industry of the business. Business can only have one primary code.
Businesses can also have up to five secondary SIC codes. Secondary SIC code classify other industries the business is involved in but aren’t the main focus. The secondary industries might overlap with your main industry or they might be unrelated.
4-Digit SIC Code
The traditional USA SIC Code is a four-digit numerical system. This compact structure is designed to represent a specific industry and its primary activities. It has the disadvantage of allowing only 9999 classes, which does not allow detailed classification.
Example: SIC Code 3571 refers to Electronic Computers.
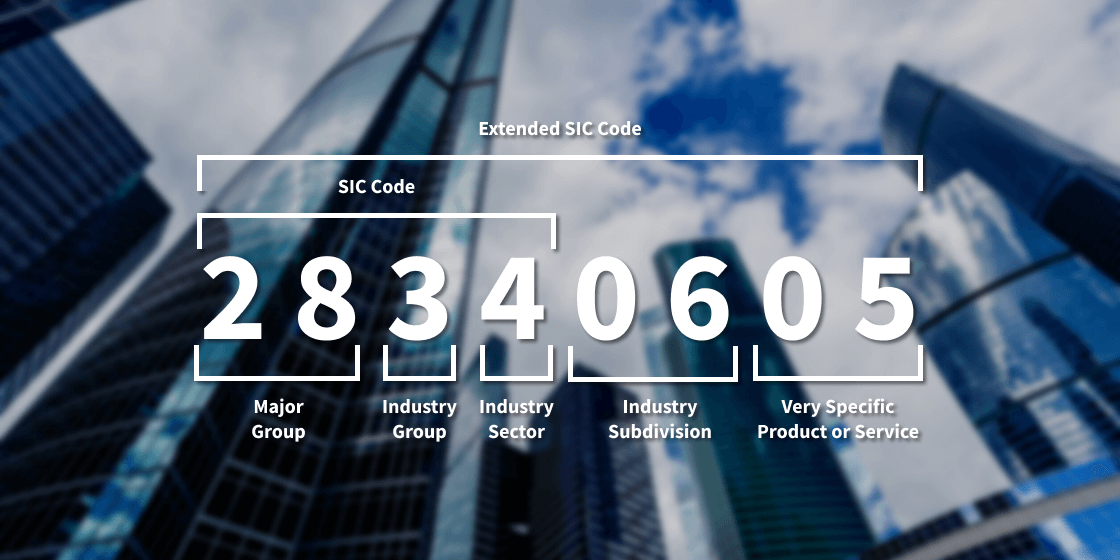
Extended 6,7 and 8-Digit SIC Code
While the original 4-digit SIC Code system was established by the U.S. government, the extended 8-digit version is a product of private sector innovation. Recognizing the limitations of the 4-digit system, private companies took the initiative to expand the SIC Code system. Their goal was to provide a more detailed classification that could cater to the nuanced and specialized nature of contemporary businesses.
This format retains the foundational 4-digit structure but adds an additional four digits to provide a granular insight into sub-industries and specific business activities.
Example: An 8-digit code such as 28340605 is a testament to the system's ability to cater to very niche sectors within the overarching industry.
SIC Code UK
The UK SIC Code is designed to categorize businesses by the type of economic activity in which they are engaged. This classification system is crucial for statistical analysis, government reporting, and business benchmarking in the UK.
The UK's Office for National Statistics (ONS) is responsible for maintaining and updating the SIC system in the UK, ensuring its relevance and accuracy in the ever-evolving business landscape.
Structure and Format
The UK SIC Code is a five-digit numerical system. Each digit in the code provides insight into the hierarchical classification of the business activity:
- Broad Industry Sectors: The initial digits give a general overview of the industry sector.
- Detailed Activities: As you progress through the digits, they offer a more granular classification, narrowing down to specific business activities or specializations.
Example: A code like 01110 pertains to a specific activity within the broader agricultural sector. While we'll delve deeper into the intricacies of each digit in subsequent sections, this example showcases the hierarchical nature of the UK SIC Code.
NAICS Codes vs. USA's SIC Codes: A Comparative Analysis
When diving into industry classification codes, two prominent systems emerge in the U.S.: the Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) and the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS). Both systems, at their core, aim to categorize industries based on their primary activities, but they do so with different methodologies.
The SIC system operates with a 4-digit code structure. However, its extended version can delve deeper, reaching up to 8 digits. This depth allows for a nuanced classification, catering to even the most specific sectors. On the other hand, NAICS Code, a more recent entrant, structures its codes ranging from 2 to 6 digits. While this structure provides a broad overview and captures a wide range of industries, it might not always offer the granularity that some businesses seek.
This brings us to the pivotal question: which system is superior? For businesses and analysts who prioritize detailed industry classification, the Extended SIC Codes often stands out as the preferred choice. Its ability to provide unparalleled granularity makes it an invaluable tool. Whether you're a niche sector trying to pinpoint your exact industry subset or a researcher aiming for precision in data analysis, the Extended SIC Code's depth and specificity cater to these needs effectively.
The table below presents a comparative view of equivalent codes for the same specific communications sector according to the Standard Industrial Classification (SIC), the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) and extended SIC systems.
| Classification System | Code | Description |
| SIC | 4841 |
Cable and Other Pay Television Services
|
| NAICS | 515210 |
Cable and Other Subscription Programming
|
| 517311 |
Wired Telecommunications Carriers
|
|
| Extended SIC |
4841-01 |
Television-Cable & Catv
|
| 4841-03 |
Satellite Comms Services-Common Carrier
|
|
| 4841-04 |
Television-Cable & Catv Equipment & Supplies
|
|
| 4841-05 |
Television Syst-Closed Circuit Tlcstng
|
|
| 4841-07 |
Satellite Descrambling/Programming Service
|
|
| 4841-09 |
Captioning Services-Television
|
|
| 4841-10 | Television IPTV | |
| 4841-11 |
Media Streaming Service
|
The Extended SIC classification system stands out for its ability to provide a nuanced breakdown of industries into more specific sectors. This granularity is invaluable for businesses, analysts, and researchers seeking a precise understanding and representation of different segments within an industry, making Extended SIC a superior choice for detailed industry classification.
How Do You Read a SIC Code?
UNDERSTANDING THE SIC CODE US
The USA SIC Code, both in its traditional 4-digit format and its extended 8-digit version, offers a systematic way to classify industries based on their primary business activities. Let's break down the structure of these codes.

4-Digit SIC Code
The traditional 4-digit SIC Code provides a hierarchical classification of industries:
- First Digit: Represents a major industry sector. It's the broadest level of classification.
- Second and Third Digits: These digits narrow down the industry group within the major sector.
- Fourth Digit: This is the most specific level of classification, detailing the industry's niche or specialization.
|
0100-0999 |
Agriculture, Forestry, Fishing |
|
1000-1499 |
Mining |
|
1500-1799 |
Construction |
|
1800-1999 |
Not used |
|
2000-3999 |
Manufacturing |
|
4000-4999 |
Transportation, Communications, Utilities |
|
5000-5199 |
Wholesale Trade |
|
5200-5999 |
Retail Trade |
|
6000-6799 |
Finance, Insurance, Real Estate |
|
7000-8999 |
Services |
|
9100-9729 |
Public Administration |
|
9900-9999 |
Nonclassifiable |
Extended 6, 7 & 8-Digit SIC Code
In some cases, the SIC code begins with a letter, which represents the category in which the code is found. For example, the letter D represents "Manufacturing", so all codes beginning with D mean that they are in the Manufacturing division.
The 6, 7 & 8-digit SIC Code offers a more granular classification:
- First Four Digits: These remain consistent with the traditional 4-digit SIC Code, representing the primary industry and its specialization. For example 3590 refers to commercial machinery.
- Fifth and Sixth Digits: These digits often represent a further subdivision within the industry.
- Seventh and Eighth Digits: Typically reserved for very specific product lines or services within the defined sub-industry.
- Letter: In some cases, the code contains a letter at the beginning. It represents the division of economic activity. Each letter corresponds to a broad industry sector.
For example, a pension fund company would use SIC code H63710101, which reads as follows:
- H is the letter for the Finance, Insurance and Real Estate division
- The 4 digits 6371 refer to the main industrial group Pension, Health and Social Fund
- The next two digits 01 correspond to the Pension industrial group
- The last two digits 01 determine the Pension Fund industry
UNDERSTANDING THE SIC CODE UK
In some cases, the SIC code begins with a letter, which represents the category in which the code is found. For example, the letter C represents "Manufacturing", so all codes beginning with C mean that they are in the Manufacturing division.
Every SIC code is composed of a letter and 4 to 5 digits:
- The letters from A to U designate the main section
- The first two digits correspond to the division
- The 3rd digit defines the group.
- The 4th digit indicates the class.
- The last number preceded by a slash refers to the subcategory. It is not present in all codes.
For instance, a company active in pension funds would have the code K65.30.
|
A |
01-03 |
Agriculture, forestry and fishing |
|
B |
05-09 |
Mining and quarrying |
|
C |
10-33 |
Manufacturing |
|
D |
35 |
Electricity, gas, steam and air conditioning supply |
|
E |
36-39 |
Water supply; sewerage, waste management and remediation activities |
|
F |
41-43 |
Construction |
|
G |
45-47 |
Wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and motor cycles |
|
I |
49-53 |
Accomodation and Food Service Activities |
|
H |
55-56 |
Transport and storage |
|
J |
58-63 |
Information and communication |
|
K |
64-66 |
Financial and insurance activities |
|
L |
68 |
Real Estate Activities |
|
M |
69-75 |
Professional, scientific and technical activities |
|
N |
77-82 |
Administrative and support service activities |
|
O |
84 |
Public administration and defence; compulsory social security |
|
P |
85 |
Education |
|
Q |
86-88 |
Human health and social work activities |
|
R |
90-93 |
Arts, entertainment and recreation |
|
S |
94-96 |
Other service activities |
|
T |
97-98 |
Activities of households as employers; undifferentieated goods- and services-producing activities of households for own use |
|
U |
99 |
Activities of extraterritorial organisations and bodies |
How Do Business and Governments Use SIC Codes?
Companies and government agencies use SIC codes differently.
SIC CODE FOR COMPANIES
The private sector uses this nomenclature to identify competitors and their customers. Businesses include their SIC code in various official documents, such as the VAT return. They also need it for various procedures such as applying for government contracts and loan application.
SIC CODE FOR GOVERNMENTS
Government agencies use SIC codes for statistical purposes. This common classification allows a clear identification of the activity of the companies. This facilitates the work of administrations such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) or Companies House.
What Is the Difference Between a NACE Code and a SIC Code?
NACE (Statistical Classification of Economic Activities in the European Community) and SIC (Standard Industrial Classification) codes are both used to classify companies according to their main activity. The former are the reference nomenclature in the European Union; the latter are used in the United States and in the United Kingdom.
The British classification has been revised in parallel with the NACE nomenclature. It is therefore easy to find a match between a company's SIC code and its NACE code.
Discover our dedicated tool and save time in just a few clicks!
Marketing SIC Code
This classification system has a major marketing advantage. One of the most significant advantages of using SIC codes for marketing is the ability to precisely target specific industries. This targeted approach allows for more effective marketing campaigns and better alignment with the unique needs and interests of each industry.
Here's a step-by-step explanation of how to target specific industries using SIC codes:
- Identify the Industry of Interest: Start by determining the specific industry or industries you want to target. This could be based on your product or service offering, market research, or business goals.
- Research Relevant SIC Codes: Find the SIC codes associated with the industry you've identified.
- Build a Targeted Prospect List: Compile a list of businesses within the industry using the relevant SIC codes. You can access business directories, industry association websites, or commercial databases to identify potential clients or partners.
- Tailor Your Marketing Messages: Create marketing messages that resonate with the specific industry's needs and challenges.
- Select Industry-Specific Marketing Channels: Choose marketing channels that are known to reach the professionals or businesses within the target industry.
- Personalize Outreach: When reaching out to potential clients or partners, make your communication personal and industry-relevant. Demonstrate your industry expertise by showcasing a deep understanding of the industry's distinct requirements, obstacles, and prospects.
- Measure and Adjust: Track the performance of your marketing campaigns. Monitor metrics like lead generation, conversion rates, and return on investment (ROI) for your targeted industry marketing efforts. Based on the results, adjust your strategy as needed to optimize your outreach.

Conclusion
SIC codes, whether in the US or the UK, serve as an essential tool for businesses, governments, and researchers alike. These codes offer a systematic and hierarchical classification of industries based on primary business activities. From the realm of marketing to government statistics, SIC codes help in identifying, categorizing, and analyzing industries. As industries evolve, so does the need for more granular classifications.
While SIC codes remain foundational, the emergence of extended versions showcases the ever-evolving nature of business operations and the need for detailed data classification. Whether it's comparing it to the EU's NACE code or understanding its significance in a digital age, SIC codes are undeniably invaluable.




Comments